總結
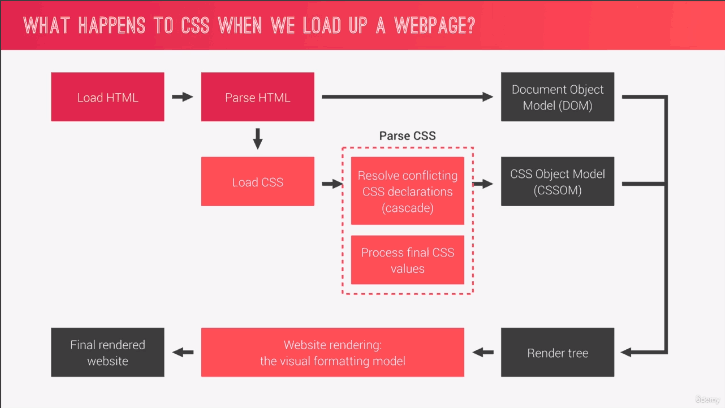
Udemy 的 Advanced CSS and Sass 在講解網頁載入 CSS 時提到關鍵字「visual formatting model」,此篇為閱讀相關文件後針對 visual formatting model 整理的筆記
筆記
這是什麼?
- It is an algorithm that how elements in the document tree are processed for visual media (such as computer screen).
- It describes how user agents take the document tree, and process and display it for visual media.
- In the visual formatting model, each element in the document tree generates zero or more boxes according to the box model. The layout of these boxes is governed by:
- box dimensions and type.
- positioning scheme (normal flow, float, and absolute positioning).
- relationships between elements in the document tree.
- external information (e.g., viewport size, intrinsic dimensions of images, etc.).
- 是 CSS 的一種規則,規定 boxes 在瀏覽器上的排列、以及 boxes 如何影響彼此的位置
結論:visual formatting model 決定一個元素會如何呈現在畫面上
什麼影響元素排序?
Box dimensions
- What is box dimensions: Each box has a content area (e.g., text, an image, etc.) and optional surrounding padding, border, and margin areas.
Box type
- A box’s type affects its behavior (layout) in the visual formatting model.
- The
displayproperty specifies a box’s type. 透過display可以設定 box model 的類別 - 設定為
display: none;時會有以下特性:- This value causes an element to not appear in the formatting structure (i.e., in visual media the element generates no boxes and has no effect on layout).
- Descendant elements do not generate any boxes either.
- The element and its content are removed from the formatting structure entirely.
- This behavior cannot be overridden by setting the ‘display’ property on the descendants.
- A display of
nonedoes not create an invisible box; it creates no box at all.
Positioning schemes
CSS 2.1 有三種 positioning schemes:
- Normal flow
- block formatting of block-level boxes
- inline formatting of inline-level boxes
- relative positioning of block-level and inline-level boxes
- Floats
- In the float model, a box is first laid out according to the normal flow, then taken out of the flow and shifted to the left or right as far as possible.
- Content may flow along the side of a float.
- Absolute positioning
- In the absolute positioning model, a box is removed from the normal flow entirely (it has no impact on later siblings) and assigned a position with respect to a containing block.
Normal flow
- Boxes in the normal flow belong to a formatting context, which may be block or inline, but not both simultaneously.
- In a block formatting context, boxes are laid out one after the other, vertically, beginning at the top of a containing block.
- In an inline formatting context, boxes are laid out horizontally, one after the other, beginning at the top of a containing block.
- The width of a line box is determined by a containing block and the presence of floats.
- The height of a line box is determined by the rules given in the section on line height calculations.
- A line box is always tall enough for all of the boxes it contains. However, it may be taller than the tallest box it contains (if, for example, boxes are aligned so that baselines line up).
- When the height of a box B is less than the height of the line box containing it, the vertical alignment of B within the line box is determined by the
vertical-alignproperty. - When the total width of the inline-level boxes on a line is less than the width of the line box containing them, their horizontal distribution within the line box is determined by the
text-alignproperty.
Floats
- A floated box is shifted to the left or right until its outer edge touches the containing block edge or the outer edge of another float.
- Since a float is not in the flow, non-positioned block boxes created before and after the float box flow vertically as if the float did not exist.
- However, the current and subsequent line boxes created next to the float are shortened as necessary to make room for the margin box of the float.
clearproperty: indicates which sides of an element’s box(es) may not be adjacent to an earlier floating box.
position property
- static:
- The box is a normal box, laid out according to the normal flow.
- The
top,right,bottom, andleftproperties do not apply.
- relative:
- The box’s position is calculated according to the normal flow, then the box is offset relative to its normal position. 根據 normal flow 的位置來進行偏移
- When a box B is relatively positioned, the position of the following box is calculated as though B were not offset. 鄰近元素會根據偏移前的原始位置來排序
- The effect of
position:relativeon table-row-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row, table-column-group, table-column, table-cell, and table-caption elements is undefined.
- absolute:
- The box’s position (and possibly size) is specified with the
top,right,bottom, andleftproperties. These properties specify offsets with respect to the box’s containing block. 設定為position: absolute;元素的位置與尺寸會被 top/right/bottom/left 影響 - Absolutely positioned boxes are taken out of the normal flow. This means they have no impact on the layout of later siblings. 排序脫離 normal flow,無法影響鄰近元素的排序
- Absolutely positioned boxes have margins, they do not collapse with any other margins.
- The box’s position (and possibly size) is specified with the
- fixed:
- In the case of handheld, projection, screen, tty, and tv media types, the box is fixed with respect to the viewport and does not move when scrolled.
- In the case of the print media type, the box is rendered on every page, and is fixed with respect to the page box, even if the page is seen through a viewport (in the case of a print-preview, for example).
- For other media types, the presentation is undefined.
Relationships between display, position, and float
- If
display: none;, thenpositionandfloatdo not apply. In this case, the element generates no box. - Otherwise, if
positionhas the valueabsoluteorfixed, the box is absolutely positioned, the computed value offloatisnone - Otherwise, if
floathas a value other thannone, the box is floated.