總結
此篇為 CSS cascading 與 specificity 的相關筆記,來源為 W3C、MDN 與 CSS-Tricks 文章
The cascade and specificity are mechanisms that control which rule applies when there is such a conflict.
筆記
Introduction
- One of the fundamental design principles of CSS is cascading, which allows several style sheets to influence the presentation of a document.
- When different declarations try to set a value for the same element/property combination, the conflicts must somehow be resolved. 目的:解決樣式衝突
- The opposite problem arises when no declarations try to set a the value for an element/property combination. In this case, a value is be found by way of inheritance or by looking at the property’s initial value. 在沒有宣告樣式的時候,透過繼承(
inherit)或初始樣式(initial)來為一元素取得樣式 - The cascading and defaulting process takes a set of declarations as input, and outputs a specified value for each property on each element.
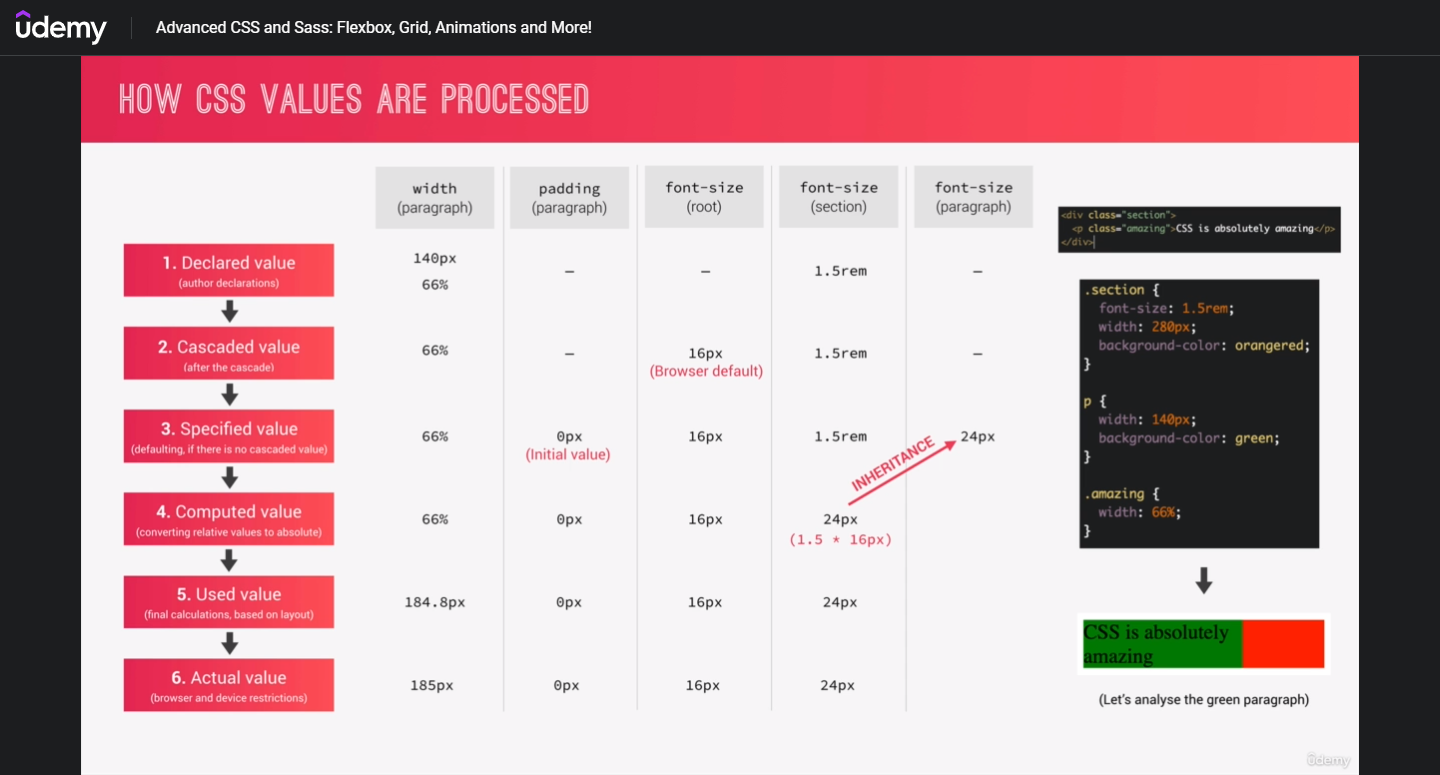
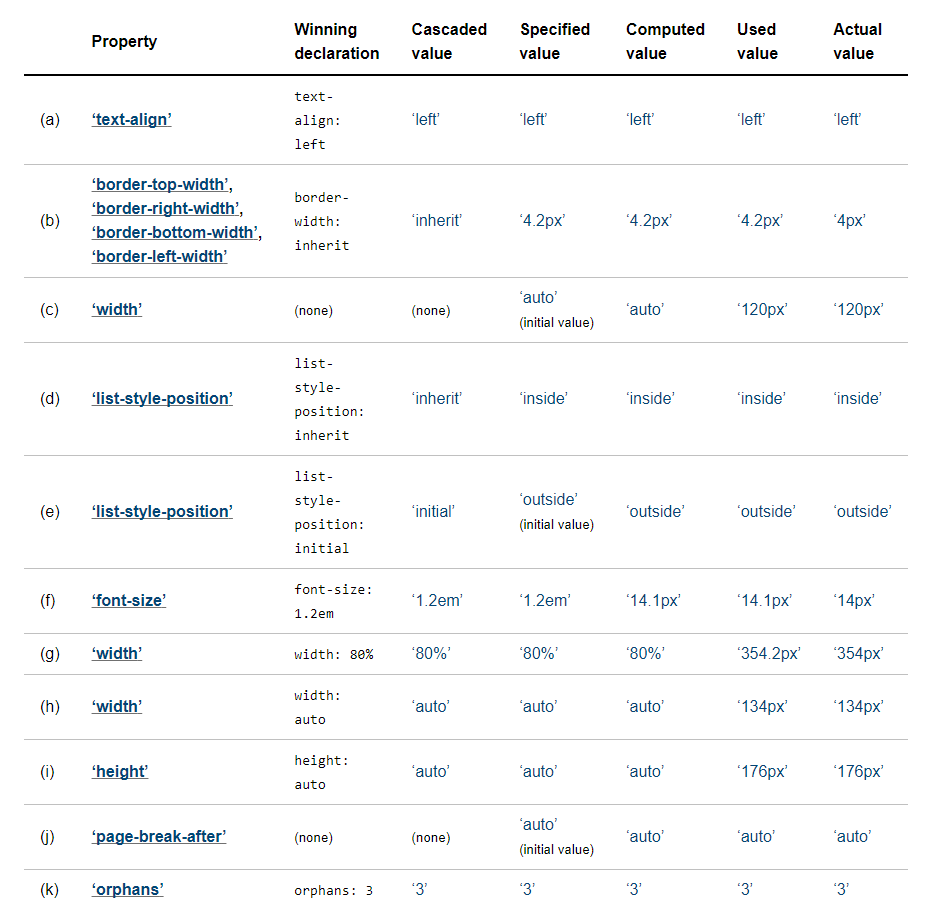
Value Processing
The final value of a CSS property for a given element or box is the result of a multi-step calculation(所有的 CSS 樣式最終都會變為以 px 為單位的數值)
-
First, all the declared values applied to an element are collected, for each property on each element. There may be zero or many declared values applied to the element. 同一個元素可能被宣告多種樣式
-
Cascading yields the cascaded value. There is at most one cascaded value per property per element. 透過 cascading 將一元素的樣式縮減為僅有一個的 cascaded value
-
Defaulting yields the specified value. Every element has exactly one specified value per property.
-
It is the result of putting the cascaded value through the defaulting processes, guaranteeing that a specified value exists for every property on every element.
-
In many cases, the specified value is the cascaded value.
-
However, if there is no cascaded value at all, the specified value is defaulted.
-
如果沒有 cascaded value 則透過 initial 或 inherit 取得樣式
-
Resolving value dependencies yields the computed value. Every element has exactly one computed value per property. 將 relative value(比如原本以 rem 為單位的數值)轉為固定數值
-
relative units: em, ex, vh, vw
-
certain keywords (e.g., smaller, bolder) must be replaced according to their definitions
-
percentages on some properties must be multiplied by a reference value (defined by the property)
-
Formatting the document yields the used value. An element only has a used value for a given property if that property applies to the element. 根據 layout 來計算 used value,比如
width: auto;要根據畫面最終 layout 才能計算出auto的實際數值 -
Finally, the used value is transformed to the actual value based on constraints of the display environment. As with the used value, there may or may not be an actual value for a given property on an element. 瀏覽器等裝置最後使用的數值
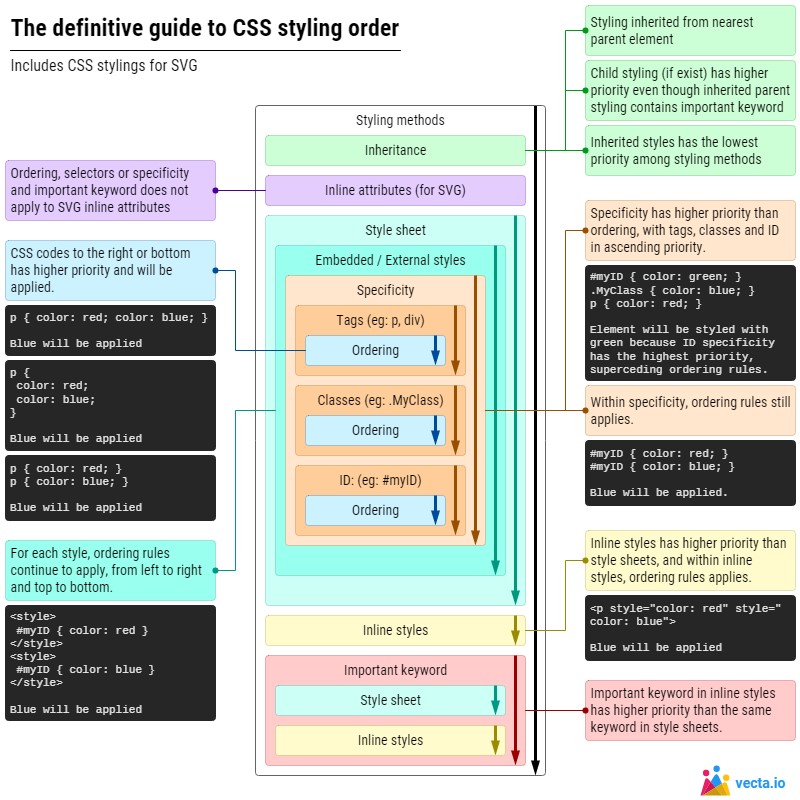
Cascade
When equal specificity, order matters.
- The cascade is an algorithm that defines how to combine property values originating from different sources.
- The CSS cascade algorithm’s job is to select CSS declarations in order to determine the correct values for CSS properties.
- Only CSS declarations, that is property/value pairs, participate in the cascade.
- Keyframes don’t cascade, meaning that at any given time CSS takes values from only one single
@keyframes, and never mixes multiple ones together. - When several keyframes are appropriate, it chooses the latest defined in the most important document, but never combined all together.
- Origin and Importance(以下權重從高至低排列,出自高順位文件的樣式會覆蓋來源為低順位的樣式)
- Transition declarations
!importantuser agent declarations!importantuser declarations!importantauthor declarations- Animation declarations
- Author declarations
- User declarations
- User agent declarations
Specificity
When different styles apply to same element, which wins.
- Specificity is the means by which browsers decide which CSS property values are the most relevant to an element and, therefore, will be applied.
- Specificity is a weight that is applied to a given CSS declaration.
- Specificity only applies when the same element is targeted by multiple declarations.
Defaulting
No cascaded value? Ask defaults.
- Inherited properties draw their defaults from their parent element through inheritance;
- The inherited value of a property on an element is the computed value of the property on the element’s parent element.
- All other properties take their initial value.
- Each property has an initial value, defined in the property’s definition table.
- If the property is not an inherited property, and the cascade does not result in a value, then the specified value of the property is its initial value.
Explicit Defaulting
除了initial與inherit以外還有另外兩種關鍵字可以使用
unset: erase all declarations- If it is an inherited property, this is treated as inherit;
- If it is not, this is treated as initial.
revert: roll back to cascade origins, the behavior depends on the cascade origin to which the declaration belongs:- author origin: Rolls back the cascaded value to the user level, so that the specified value is calculated as if no author-origin rules were specified for this property on this element.
- user origin: Rolls back the cascaded value to the user-agent level, so that the specified value is calculated as if no author-origin or user-origin rules were specified for this property on this element.
- user-agent origin: Equivalent to
unset.