總結
實作的部分因為直接使用套件connect-mongo幫忙處理,所以沒什麼難度
本篇重點放在理解 session、cookie,以及 express.js 伺服器如何保管 session
環境
connect-mongo: 4.4.1os: Windows_NT 10.0.18363 win32 x64筆記
Stateless Protocol
- HTTP 是一種 stateless protocol
- 每一筆從瀏覽器發出的 request 對伺服器來說都是互無關係的
- 可將 request 理解為銀行客戶,而伺服器是完全臉盲的行員;不管客戶來幾次,該行員就是無法主動認出「啊,這是我的客戶」,只要客戶離開櫃台,行員就會完全忘記該客戶是誰
- Stateless Protocol 的優點:
- Wikipedia: Stateless protocols improve the properties of visibility, reliability, and scalability.
- Visibility is improved because a monitoring system does not have to look beyond a single request in order to determine its full nature. 不須處理上下文
- Reliability is improved because it eases the task of recovering from partial failures. 若有錯誤發生,只需要復原出錯的部分即可
- Scalability is improved because not having to store session state between requests allows the server to quickly free resources and further simplifies implementation. 不須額外效能來記憶狀態
- 問題:如果今天要打造一個「能維持使用者登入狀態」的 Web APP,勢必需要其他技術協助
關於 sessions
-
sessions不是Chrome DevTools 打開來切換到 Application 分頁看到的 session storage
-
sessions 儲存在伺服器端,不存在使用者的瀏覽器中
- 而 sessions 實際究竟儲存在 Express.js 伺服器的「哪裡」則是根據開發者的設定決定
- 參考「Where does express js save session details?」,在沒有任何設定的情況下,Express.js 伺服器會把 sessions 儲存在 RAM 中,所以重啟伺服器後,已登入的使用者也會被踢回登入畫面
- 而如果把 sessions 保存在 Redis 或 MongoDB 等資料庫裡面的話,重啟 Web APP 的伺服器也不會失去 sessions 資料,已登入的使用者會繼續維持登入狀態
-
- 參考「Understanding Sessions and Local Authentication in Express with Passport and MongoDb」
- An Express.js middleware used for persisting sessions across stateless HTTP requests.
- Sessions are used for storing data about a user and presenting dynamic data based on a user’s identity. They rely upon saving session data to a cookie that is sent to the user’s browser and then received back in future user requests.
- This module expands the Express.js
requestobject with thesessionproperty (among other things), which itself is an object that can be used by other middleware. - By default it uses a
MemoryStore, an in-memory key-value database not intended for production use, to store the session data. But you can and should plug in another memory store middleware when deploying a serious product.
關於 cookies
- 保存在使用者的瀏覽器中,開啟 Chrome 瀏覽器的 DevTools 切換到 Application 分頁,即可看到 cookies
- cookies 內容是可以隨意被使用者修改的(儘管修改 cookie 極可能讓該 cookie 直接失效)
- cookies 夾帶在瀏覽器對伺服器發出的 request header 中
- MDN: After receiving an HTTP request, a server can send one or more Set-Cookie headers with the response. The cookie is usually stored by the browser, and then the cookie is sent with requests made to the same server inside a Cookie HTTP header.
- An expiration date or duration can be specified, after which the cookie is no longer sent. cookies 是可以設定有效期限的
- Additional restrictions to a specific domain and path can be set, limiting where the cookie is sent. 可以限制 cookies 僅能被送到哪些 domain 或 path
實作
產出 sessions
- 第 8 行:根據使用者輸入的 email,從資料庫中取出相對應的使用者資料來比對密碼
- 第 16 行:將
user.id的值賦予req.session.passport.user- passport.serializeUser(fn(user, done) | fn(req, user, done)): Passport will call this to serialize the user to the session whenever you login a user with
req.login(), or whenever a user is authenticated viapassport.authenticate(). The function you pass in should calldone(null, serializedUser). - What this is going to do is set
req.session.passport.user = serializedUser. Traditionally you’d makeserializedUsersome sort of string, like a user ID which you can fetch from your DB. - Understanding passport.js authentication flow:
passport.serializeUsercan access the user object we passed back to the middleware. Its job is to determine what data from the user object should be stored in the session. The result of the serializeUser method is attached to the session asreq.session.passport.user = { // our serialized user object // }. The result is also attached to the request asreq.user.
- passport.serializeUser(fn(user, done) | fn(req, user, done)): Passport will call this to serialize the user to the session whenever you login a user with
保存 sessions 至資料庫中
使用測試帳號登入後,即可在資料庫中看到 sessions 被保存下來:
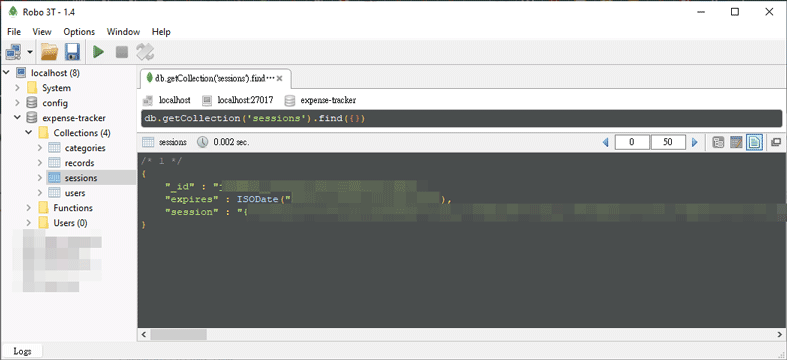
因 sessions 被另外保存到資料庫中,日後即使 Web APP 的伺服器重啟,也不會遺失使用者的登入狀態