總結
問:JPEG 到底是什麼? 答:實際上是一種壓縮影像的演算法
問:JPEG 如何壓縮影像? 簡答:將影像從 RGB 轉換為 Y’CbCr,捨棄多餘的顏色資訊、壓縮人眼不易察覺的部分(影像中高頻率變化的部分)後,輸出為.jpg 檔案
內收關於影片組「How JPEG Works」的相關筆記、JPEG 詳細的壓縮過程,與其他參考資料來源。
Part 0: color spaces
Color spaces
- Color spaces are the ways of representing the colors in an image
- RGB: red, green and blue; most monitors use this format
- Y’CbCr: use by high definition video, TV broadcasting, JPEG
- CMYK: cyan, magenta, yellow and black; printers use this format
- 01:48 用 K 來代表黑色是因為 B 已經被藍色(blue)使用了
Y’CbCr
- Y’: luminosity from 0 to 255;明亮的程度
- Cb/ Cr: blue/ red chrominance values from -127 to 128;藍色/紅色的濃度
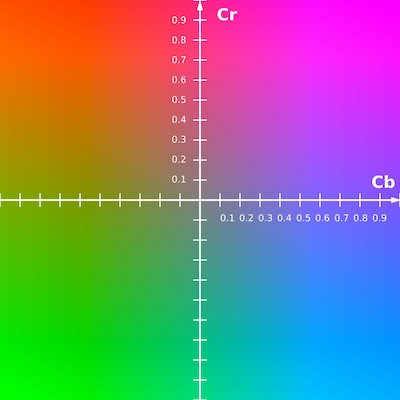
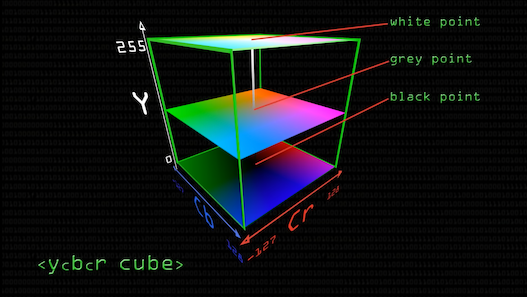
- 05:58 開始:
- You’ll generally use Y’CbCr if you’re doing any kind of TV broadcasting.
- If you’re actually sending a stream of data to someone’s TV, you need to worry about how much compression you have about data, because it’s quite important.
- Y’CbCr lets you do very clever techniques by down sampling the color components, but not down sampling the luminous component; people won’t really notice this… in fact, this is the fundamental to how JPEG works.
- Wiki: This reflects the fact that human eye is less sensitive to fine color details than to fine brightness details.
- 人眼「對明亮變化的察覺程度」大於「對顏色變化的察覺程度」
- Y’CbCr 將影像的「明亮度資訊」與「顏色資訊」分開來
- 捨棄一定程度顏色的資訊,但盡量保留影像的明亮度資訊的話,即使經過壓縮,人眼也不太容易察覺壓縮前後的差異
- JPEG 就是使用這樣的原理來壓縮圖片的
Part 1: files and color
JFIF
- JPEG 實際上並不是檔案格式,而是壓縮影像的方式;JFIF 才是檔案格式
- JPEG File Interchange Format (JFIF) is the actual wrapper that holds the compress data.
- (Wiki) JFIF is an image file format standard, the most common format for storing and transmitting photographic images on the World Wide Web.
- (Wiki) JFIF defines supplementary specifications for the container format that contains the image data encoded with the JPEG algorithm.
- 01:07 …really, when we’re talking about a JPEG file, we’re actually talking about a JFIF file most of the time.
frequency
- 01:30 開始:
- …we don’t see high-frequency changes in image intensity very well either. So we can get rid of some of that high-frequency information.
- Bits of image that change intensity very very quickly, we can kind of sorta blur out, and those things will go away, we won’t really see a difference.
筆記:人眼對於高頻率的變化並不敏銳,所以影像裡面高頻率的部分可以捨棄(壓縮)。 影像的頻率:指「像素變化」的程度。 使用越少的像素完成變化,頻率越高;使用越多的像素完成變化,頻率越低。
- Let’s say you have some region in your image that changes from white to black. If it takes many pixels to undergo that change, it’s low frequency. The fewer the pixels it takes to represent that intensity variation, the higher the frequency. Ref.: What are the low and high frequencies in an image?
- Frequency means rate of change of something. In two-dimensional signals like digital images, frequencies are rate of change of grey scale value (intensity of pixel) with respect to space. This is also called Spatial frequency. Ref.: What are frequencies in images?
- One interesting application is in the use of compression algorithms like JPEG. Here the DCT (Discrete cosine transform) is used to save more of the important parts of the image (the low frequencies) and less of the high frequencies. Ref. What does “frequency” mean in an image?
- Wiki: Human vision is much more sensitive to small variations in color (or brightness) over large areas than to the strength of high-frequency brightness variations.
補充:對人眼來說,察覺「大範圍中小小的顏色或亮度變化」比發現「高頻率的亮度變化」容易。
Compression steps
- Transform the image into Y’CbCr color space
- Y’CbCr separate each pixel’s intensity (Y’) from color (Cb, Cr)
- Down-sampling (chroma sub-sampling)
- Wiki: reduce the spatial(空間性的) resolution of the Cb and Cr components
- 白話文:減少影像使用的顏色數量
- Block splitting
- Wiki: depending on chroma sub-sampling, this yields Minimum Coded Unit (MCU) blocks of size 8×8 (4:4:4 when no sub-sampling), 16×8 (4:2:2), or most commonly 16×16 (4:2:0).
- Apply DCT (discrete cosine transform)
- Quantization (the lossy part in JPEG compression)
- Huffman encoding, get the .JPG file
Down-sampling
- 04:37 開始:
- One of the nice things about Y’CbCr is that human eye doesn’t really see chrominance very well. It’s certainly a much lower resolution than we see changes in intensity.
- Just like with TV encoding, we can massively down sample the amount of Cb and Cr that we see in the image.
- 06:14 Down-sampling is sometimes tied to the quality of the JPG that you output.
- 影像軟體在輸出.JPG 檔案時,「品質」調整的通常就是 down-sampling 的程度
- 06:29 In general, most software will use a down-sample of 2 in both direction, which is 4 times less colors.
Part 2: DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform)
DCT
- 02:53 …in JPEG, we can get rid of some of the higher frequency signals and the general gist of the image will still be there.
- 03:19 What we do in JPEG is we split each image into 8 by 8 pixel groups, and each of those pixel groups is separately encoded with its own discrete cosine transform.
- Wiki:
- Each 8 by 8 pixel group is converted to a frequency-domain representation by “normalized, two-dimensional type-II DCT”.
- Before computing the DCT of the pixel group, its values are shifted from a positive range to one centered on zero (from
[0, 255]to[-128, 127]). This step reduces the dynamic range requirements in the DCT processing stage that follows.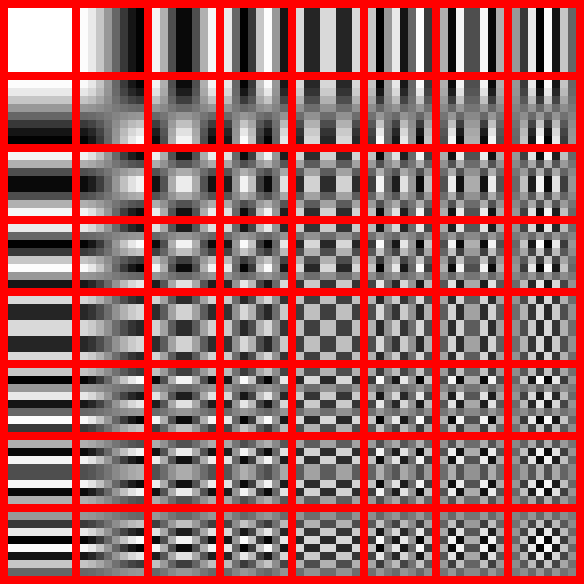
- The DCT transforms an pixel group of input values to a linear combination of these 64 patterns (see above image). The output values are referred to as transform coefficients.
Quantization
- 08:27 After calculating the discrete cosine transform coefficients, we will try to remove the ones we don’t want. We call the process of removing the high frequency data “quantization”.
- Wiki: the elements in the quantization matrix control the compression ratio, with larger values producing greater compression.
- 白話文:DCT 結束後得到的transform coefficients會根據 quantization matrix 繼續壓縮。quantization matrix 會指示transform coefficients中每一個像素被壓縮的程度;quantization matrix 中越大的數字代表越大的壓縮比例
- 12:55 If we increase the values in the quantization table, we’re essentially operating a lower JPEG quality setting.
Quantization matrix (quantization table)
Wiki: the quantization matrix is designed to provide more resolution to more perceivable frequency components over less perceivable components (usually lower frequencies over high frequencies) in addition to transforming as many components to 0, which can be encoded with greatest efficiency.
白話文:quantization matrix 會盡可能保留人眼可察覺的部分(通常是低頻率的部分),捨棄人眼察覺不出來的部分(高頻率的部分)
Huffman encoding
- 以 zigzag 的形式來編碼transform coefficients
- transform coefficients中,通常是左上角擁有較多資訊,而右下角偏向被捨棄,搭配 Huffman encoding 可以讓尾部大量的 0 一起被壓縮
- 10:34 We serialize them out into a long line, and we use Huffman encoding to shrink them right down.