總結
此為「Inside look at modern web browser」四部曲文章的相關筆記。 註:本篇筆記內的圖片除了以下這張之外,全部都是從「Inside look at modern web browser」系列取得的說明圖片。
第一部:架構 Architecture
Process 與 Thread
- 在電腦(或手機)上開啟瀏覽器應用程式後,電腦(或手機)會建立一個 process,並分配記憶體空間給該 process。
- 一個 process 裡面可以包含多個 thread。
- 一個 process 可以要求電腦(或手機)建立另外一個 process 來幫忙,而 process 之間透過 IPC 來溝通。
A process can be described as an application’s executing program. A thread is the one that lives inside of process and executes any part of its process’s program. Wikipedia: In computing, a process is the instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many threads.
Process 中可能有一個或複數個 Thread。
When you start an application, a process is created. The program might create thread(s) to help it do work, but that’s optional. The Operating System gives the process a “slab” of memory to work with and all application state is kept in that private memory space. When you close the application, the process also goes away and the Operating System frees up the memory.
「開啟應用程式」代表建立一個 process,而計算機的 OS 會分配記憶體中的一些空間給該 process;當使用者結束該應用程序後,那個 process 使用的記憶體空間就會被釋放。
A process can ask the Operating System to spin up another process to run different tasks. When this happens, different parts of the memory are allocated for the new process. If two processes need to talk, they can do so by using Inter Process Communication (IPC).
Process 可以請 OS 再建立另一個 process 來處理其他任務,而不同的 process 彼此使用 IPC 來互相溝通。
瀏覽器架構
- 不同廠牌的瀏覽器會有不同的架構。
- 以 Chrome 為例,其架構可拆為 browser process、renderer process、plugin process 與 GPU process 等等。
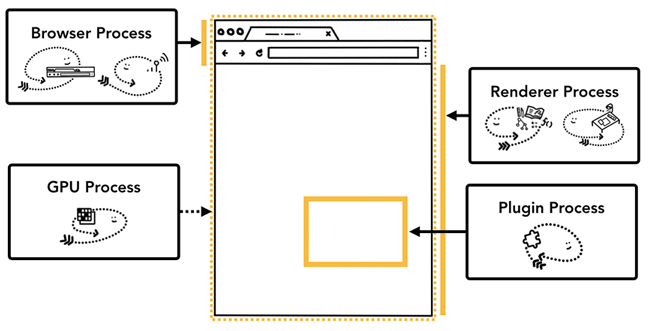
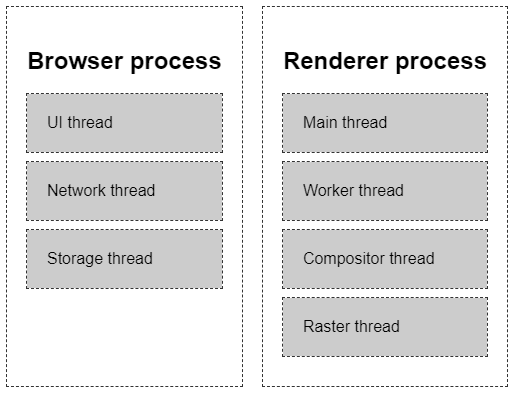
- browser process 負責的是「Chrome 這個應用程式中『不是 web content』的部分」。其中包含 UI thread、Network thread 與 Storage thread 等等。
Controls “chrome” part of the application including address bar, bookmarks, back and forward buttons. Also handles the invisible, privileged parts of a web browser such as network requests and file access.
- renderer process 負責的是「Chrome 這個應用程式中『屬於 web content』的部分」。
Controls anything inside of the tab where a website is displayed.
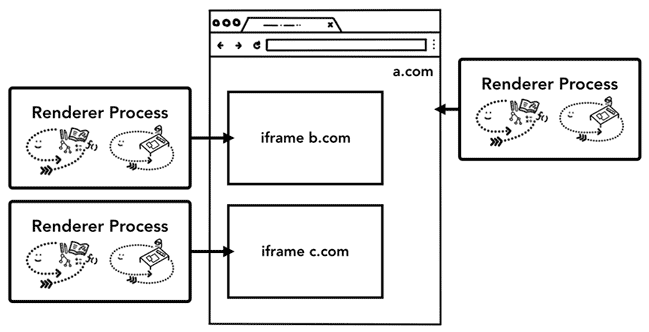
- 一個 tab 可能會有複數個 renderer processes,因為 Chrome 現行的架構是:「一個網站(包含 iframes)分配一個 process」。
- browser process 負責的是「Chrome 這個應用程式中『不是 web content』的部分」。其中包含 UI thread、Network thread 與 Storage thread 等等。
第二部:導航 Navigation
browser process
The browser process has threads like the UI thread which draws buttons and input fields of the browser, the network thread which deals with network stack to receive data from the internet, the storage thread that controls access to the files and more.
- UI thread:負責處理「使用者可以鍵入關鍵字、或直接輸入 URL 來前往特定網站」的輸入區塊(input fields)。
- Network thread:處理「向網路索取資料」的相關工作。
- Storage thread:處理「檔案存取權限」的相關工作。
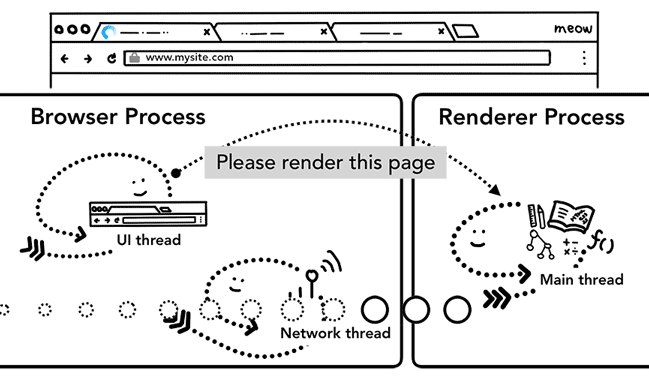
When you type a URL into the address bar, your input is handled by browser process’s UI thread.
當一個使用者在瀏覽器的輸入區塊鍵入 URL 後,「使用者輸入的資料」就是由 UI thread(隸屬於 browser process)負責處理的。
流程
- 當使用者在輸入區塊鍵入資料後,UI thread 首先要辨別該資料是「URL(使用者要前往特定網頁)」還是「關鍵字(使用者要查找資料)」。
- UI thread 要決定它應該「呈現特定網頁」或是「呈現搜尋結果」給使用者看。
- 如果使用者輸入的是 URL,UI thread 會發起 network call,通知 Network thread 去取得網頁內容,這時 Network thread 會使用相對應的 protocols 來與伺服器建立連線。
When a user hits enter, the UI thread initiates a network call to get site content.
- 注意:如果伺服器回覆 HTTP 301(Moved Permanently)給 Network thread 的話,Network thread 會通知 UI thread:「伺服器要求重新導向」,此時 UI thread 會發一個新的 URL request 給 Network thread。
At this point, the network thread may receive a server redirect header like HTTP 301. In that case, the network thread communicates with UI thread that the server is requesting redirect. Then, another URL request will be initiated.
- Network thread 從伺服器收到資料後,它會檢查該資料的 content-Type header,以便知道伺服器究竟提供了什麼類型的資料。
- 但 content-Type header 中自稱的資料類型可能是錯的。
- 這時候需要執行 MIME Type sniffing 來確認資料類型。
MIME Type sniffering:inspecting the content of a byte stream to attempt to deduce (推斷) the file format of the data within it.
- 如果資料內容是 HTML 檔案,且檔案內容經過檢查、看起來安全的話,Network thread 會告訴 UI thread「資料已經準備好了」(注意這兩個 threads 都還在 browser process 內),然後 UI thread 會去找一個 renderer process 來處理 HTML 渲染的工作。
Once all of the checks are done and Network thread is confident that browser should navigate to the requested site, the Network thread tells UI thread that the data is ready. UI thread then finds a renderer process to carry on rendering of the web page.
- browser process 會透過 IPC 來「commit the navigation」給 renderer process。
Now that the data and the renderer process is ready, an IPC is sent from the browser process to the renderer process to commit the navigation.
- browser process 也會對 renderer process 建立 data stream,以便把收到的資料交給 renderer process。
It also passes on the data stream so the renderer process can keep receiving HTML data.
- 一旦 browser process 確認 commit 在 renderer process 發生後,navigation 流程就算是結束,而 document loading 流程開始。
Once the browser process hears confirmation that the commit has happened in the renderer process, the navigation is complete and the document loading phase begins.
- tab 的 session history 會更新,這樣瀏覽器的「上一頁/下一頁」按鈕才會記住瀏覽過的頁面,而 session history 會存在硬碟中(不然 session 在關掉 tab 後就不見了)。
The session history for the tab will be updated so back/forward buttons will step through the site that was just navigated to. To facilitate tab/session restore when you close a tab or window, the session history is stored on disk.
renderer process 1
- 「navigation commit」發生後,由 renderer process 接手處理渲染畫面的工作。
- 然後當 renderer process 結束渲染工作後,它會透過 IPC 告訴 browser process 渲染完成了,這時候 browser process 內的 UI thread 會把 tag 上的 spinning 圖示停下來。
- 所謂的「渲染結束」指的是「所有的
onload事件都已經觸發且完成了」。
前往另一個網站
如果要從「目前正在瀏覽的網站」移動到「另一個網站」,流程又是如何?
- 從一個網頁 navigate 到另外一網頁「前」,要先檢查現在的網頁有沒有
beforeunload要處理。Well, the browser process goes through the same steps to navigate to the different site. But before it can do that, it needs to check with the currently rendered site if they care about
beforeunloadevent. - web content 所有的內容都歸 renderer process 管,所以 browser process 在導向新的網頁前,要先透過 renderer process 確認有沒有
beforeunload要處理。beforeunloadcan create “Leave this site?” alert when you try to navigate away or close the tab. Everything inside of a tab including your JavaScript code is handled by the renderer process, so the browser process has to check with current renderer process when new navigation request comes in. - 舊的 renderer process 會處理
unload之類的事件,新的 renderer process 會負責渲染頁面的工作。When the new navigation is made to a different site than currently rendered one, a separate render process is called in to handle the new navigation while current render process is kept around to handle events like
unload.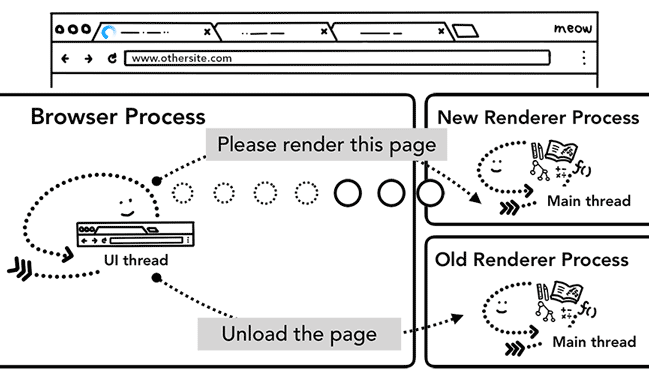
service worker
service worker 搭配Cache API可以讓應用程式即使處在沒有網路的環境下,也能進行一定程度的操作。
Service worker is a way to write network proxy in your application code; allowing web developers to have more control over what to cache locally and when to get new data from the network. If service worker is set to load the page from the cache, there is no need to request the data from the network.
那麼,提問: service worker 是 JavaScript code(由 renderer process 管轄),browser process 怎麼知道某網站會用到 service worker?
The important part to remember is that service worker is JavaScript code that runs in a renderer process. But when the navigation request comes in, how does a browser process know the site has a service worker?
回答如下:
- 透過 JavaScript 註冊 service worker 時(發生在 renderer process 中),service worker 的「scope」會被記錄下來。
- 當使用者要導覽到某個網站時,browser process 內的 Network thread 會檢查某網站「是否有註冊過 service worker」?
- 「有」的話,UI thread(屬於 browser process)會找一個 renderer process 來運行 service worker。
- render process 內的 worker thread 會決定要向網路還是快取拿資料。
When a service worker is registered, the scope of the service worker is kept as a reference. When a navigation happens, network thread checks the domain against registered service worker scopes, if a service worker is registered for that URL, the UI thread finds a renderer process in order to execute the service worker code.
The service worker may load data from cache, eliminating the need to request data from the network, or it may request new resources from the network.
第三部:渲染 Rendering
renderer process 2
The renderer process’s core job is to turn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript into a web page that the user can interact with.
renderer process 的工作:把原始碼轉換成使用者可以互動的網頁。
The renderer process is responsible for everything that happens inside of a tab. In a renderer process, the main thread handles most of the code you send to the user. Sometimes parts of your JavaScript is handled by worker threads if you use a web worker or a service worker. Compositor and raster threads are also run inside of a renderer processes to render a page efficiently and smoothly.
renderer process 包含以下幾種 thread:
- main thread:處理大部分的程式碼
- worker thread:如果有使用 web worker 或 service worker 的話,worker thread 會負責處理這些部位的 JavaScript
- compositor thread:把畫面分拆為不同的圖層(layers)
- raster thread:負責把向量圖轉換成像素圖
parsing
重點:(renderer process 中的)main thread 將 HTML 轉換為 DOM 的過程就是 parsing。
- 建立 DOM:由 main thread 把 text string (HTML)轉換為 Document Object Model (DOM)。
When the renderer process receives a commit message for a navigation and starts to receive HTML data, the main thread begins to parse the text string (HTML) and turn it into a Document Object Model (DOM).
- 導入外部資源:外部資源包括任何網頁上會用到的圖片、CSS 樣式或 JavaScript 程式碼。這些資料會由 preload scanner 統整起來,然後送去 browser process,請 network thread 幫忙處理(而不是由 renderer process 的 main thread 來請求這些資料)。
A website usually uses external resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript. Those files need to be loaded from network or cache. The main thread could request them one by one as they find them while parsing to build a DOM, but in order to speed up, “preload scanner” is run concurrently. If there are things like
<img>or<link>in the HTML document, preload scanner peeks at tokens generated by HTML parser and sends requests to the network thread in the browser process. - 不要讓 JavaScript 阻擋渲染流程:因為 JavaScript 程式碼中可能包含改變 DOM 的內容,所以瀏覽器一定要把 JavaScript 相關的內容解析完畢後、才能繼續進行畫面渲染的流程。
When the HTML parser finds a
<script>tag, it pauses the parsing of the HTML document and has to load, parse, and execute the JavaScript code. Why? because JavaScript can change the shape of the document using things likedocument.write()which changes the entire DOM structure (overview of the parsing model in the HTML spec has a nice diagram). This is why the HTML parser has to wait for JavaScript to run before it can resume parsing of the HTML document. - 換句話說,如果是與畫面渲染沒有關聯的資源,可透過加上
async或defer關鍵字來提醒瀏覽器「不用急著載入這些資料」,避免卡住瀏覽器進行畫面渲染。There are many ways web developers can send hints to the browser in order to load resources nicely. If your JavaScript does not use
document.write(), you can add async or defer attribute to the<script>tag. The browser then loads and runs the JavaScript code asynchronously and does not block the parsing. You may also use JavaScript module if that’s suitable.<link rel="preload">is a way to inform browser that the resource is definitely needed for current navigation and you would like to download as soon as possible.
style calculation
重點:建構完 DOM 後,main thread 會開始解析 CSS 樣式內容。
- 將 DOM 建構完畢後,main thread 會開始解析 CSS 樣式。
Having a DOM is not enough to know what the page would look like because we can style page elements in CSS. The main thread parses CSS and determines the computed style for each DOM node.
- Chrome 會提供 user agent stylesheet(可理解為網頁套用預設樣式,不同品牌的瀏覽器,其 user agent stylesheet 內容也會不同),所以即使一份 HTML 檔案沒有被給定任何 CSS 樣式,該網頁也不會以「完全沒有任何樣式」的模樣呈現在使用者面前。
Even if you do not provide any CSS, each DOM node has a computed style.
<h1>tag is displayed bigger than<h2>tag and margins are defined for each element. This is because the browser has a default style sheet.
- Chrome 的 user agent stylesheet 原始碼可在此查看。
layout
重點:CSS 樣式解析完畢後,main thread 開始建立 layout tree,layout tree 只會包含「要被安排在畫面上的內容」。
- 解析完 CSS 樣式後,main thread 會根據 DOM 與 CSS 樣式內容來建構 layout tree。
The layout is a process to find the geometry of elements. The main thread walks through the DOM and computed styles and creates the layout tree which has information like x y coordinates and bounding box sizes.
- layout tree 只會列出真正要顯示在畫面上的元素,亦即,如果有某個
<div>的 CSS 樣式被設定為display: none的話,該<div>是不會出現在 layout tree 中的。Layout tree may be similar structure to the DOM tree, but it only contains information related to what’s visible on the page. If
display: noneis applied, that element is not part of the layout tree (however, an element withvisibility: hiddenis in the layout tree).
paint
At this paint step, the main thread walks the layout tree to create paint records. Paint record is a note of painting process like “background first, then text, then rectangle”.
paint records:「根據特定順序分別繪製不同元素」的指令。
The most important thing to grasp in rendering pipeline is that at each step the result of the previous operation is used to create new data. For example, if something changes in the layout tree, then the Paint order needs to be regenerated for affected parts of the document.
須注意 rendering pipeline 中的資料都是承先啟後的,一旦修改了 layout tree,paint record 的資料也需要跟著變動。
compositing
Compositing is a technique to separate parts of a page into layers, rasterize them separately, and composite as a page in a separate thread called compositor thread. If scroll happens, since layers are already rasterized, all it has to do is to composite a new frame. Animation can be achieved in the same way by moving layers and composite a new frame.
compositing 的工作:把一個畫面分拆為不同的 layers,並讓每個 layer 各自 rasterize。
Turning this information into pixels on the screen is called rasterizing.
rasterizing:把向量資訊繪製成顯示裝置上的像素點。
In order to find out which elements need to be in which layers, the main thread walks through the layout tree to create the layer tree. If certain parts of a page that should be separate layer (like slide-in side menu) is not getting one, then you can hint to the browser by using will-change attribute in CSS.
Once the layer tree is created and paint orders are determined, the main thread commits that information to the compositor thread. The compositor thread then rasterizes each layer. A layer could be large like the entire length of a page, so the compositor thread divides them into tiles and sends each tile off to raster threads. Raster threads rasterize each tile and store them in GPU memory.
流程如下:
- renderer process 的 main thread 計算出 layer tree。
- main thread 把 layer tree 的資訊交給 compositor thread。
- compositor thread 對每一個 layer 進行 rasterization(向量變像素)。
- layer 如果太大,compositor thread 會把 layer 切成 tiles 後,再送進 raster thread 進行 rasterization。
Once tiles are rastered, compositor thread gathers tile information called draw quads to create a compositor frame.

tiles 從向量變像素(rasterization)後,compositor thread 會收集關於 tiles 的資訊(稱為 draw quads),以便建立 compositor frame。
- draw quads:包含「tile 在記憶體中的位置」以及「tile 要被繪製在畫面上的什麼位置」的資訊。
- compositor frame:畫面的一個 frame。
A compositor frame is then submitted to the browser process via IPC. At this point, another compositor frame could be added from UI thread for the browser UI change or from other renderer processes for extensions. These compositor frames are sent to the GPU to display it on a screen. If a scroll event comes in, compositor thread creates another compositor frame to be sent to the GPU.
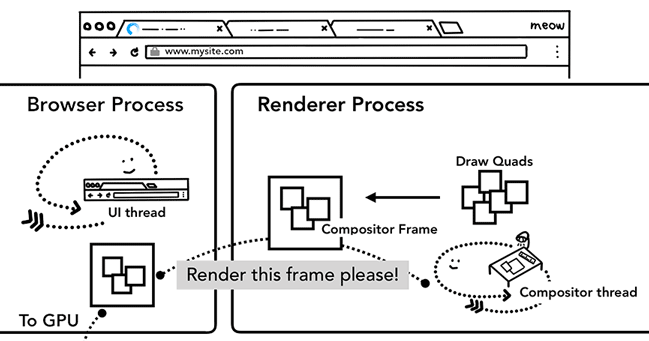
compositor frame 從 renderer process 透過 IPC 傳遞到 browser process 後,會被轉交給 GPU 來「呈現在使用者的裝置上」,直到這一步使用者才真的會「看到網頁」。
compositor-only properties
The benefit of compositing is that it is done without involving the main thread. Compositor thread does not need to wait on style calculation or JavaScript execution. This is why compositing only animations are considered the best for smooth performance. If layout or paint needs to be calculated again then the main thread has to be involved.

- 不經過 layout 與 paint(不需要 main thread),全部都由 compositing thread 處理的 CSS 樣式:
transformopacity:須注意 Blink 在處理opacity時會進入 painting 階段- 不同的 CSS 樣式各自會觸發不同廠牌瀏覽器的哪些階段,可參考:CSS Triggers
第四部:瀏覽器如何處理事件
From the browser’s point of view, input means any gesture from the user. Mouse wheel scroll is an input event and touch or mouse over is also an input event.
事件(input):瀏覽器將「使用者對網頁進行操作的行為」視為事件(input)。
- browser process 會注意到「有 input event 在 web content 上的某處發生」。
When user gesture like touch on a screen occurs, the browser process is the one that receives the gesture at first. However, the browser process is only aware of where that gesture occurred since content inside of a tab is handled by the renderer process.
- browser process 會把 event type 以及 event type 的 coordinates(座標)資訊發給 renderer process。
So the browser process sends the event type (like
touchstart) and its coordinates to the renderer process. - renderer process 會計算出 event target 是對應到畫面上的哪一個元素,以及配合該元素 event listener 的 function。
Renderer process handles the event appropriately by finding the event target and running event listeners that are attached.
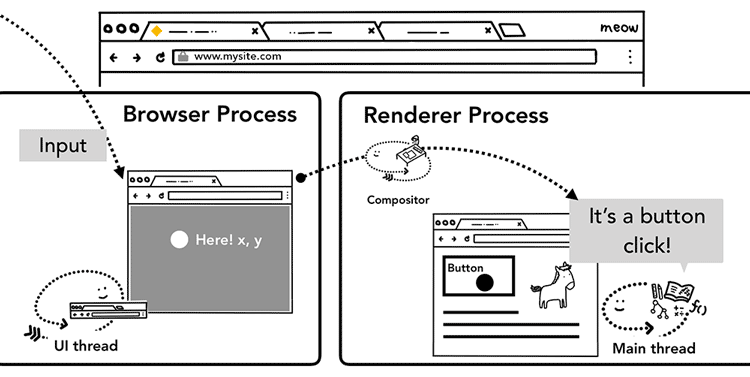
non-fast scrollable region
- compositor thread 會把帶有事件監聽器的畫面區塊標記為「non-fast scrollable region」。
Since running JavaScript is the main thread’s job, when a page is composited, the compositor thread marks a region of the page that has event handlers attached as “Non-Fast Scrollable Region”.
- 如果該區域有與使用者發生互動,compositor thread 會把互動事件發給 main thread 處理。
By having this information, the compositor thread can make sure to send input event to the main thread if the event occurs in that region.
- 如果互動事件是在「non-fast scrollable region」以外的地方發生,compositor thread 會負責產生一個新的 frame。
If input event comes from outside of this region, then the compositor thread carries on compositing new frame without waiting for the main thread.
- 事件送到 main thread 後,會執行 hit test 來確認 event target。hit test 會查詢 renderer process 在 paint 階段的資料,來知道事件到底是在哪一個元素上發生的。
When the compositor thread sends an input event to the main thread, the first thing to run is a hit test to find the event target. Hit test uses paint records data that was generated in the rendering process to find out what is underneath the point coordinates in which the event occurred.
補充
- 本文僅記錄「Inside look at modern web browser」系列文中目前能理解的部分,有機會還是請閱讀原文。
- 關於「渲染 Rendering」的細部分解可參考以下影片:
參考文件
- Inside look at modern web browser
- Wikipedia
- CSS Triggers
- Stick to Compositor-Only Properties and Manage Layer Count