原始問題
要在 HTML 檔案中使用<script>標籤載入 JavaScript 檔案時,一個常見的作法是「把<script>標籤放在<body>的最底部 (也就是</body>前)」。請問:
- 這樣做的話,在瀏覽器渲染流程中,會在什麼時機點載入到 JavaScript 程式碼?
- 為什麼需要這樣做?
- 如果我們想要「在 DOM 生成的同時,一併載入 JavaScript」,針對
script標籤還有什麼其他的處理作法?
回答
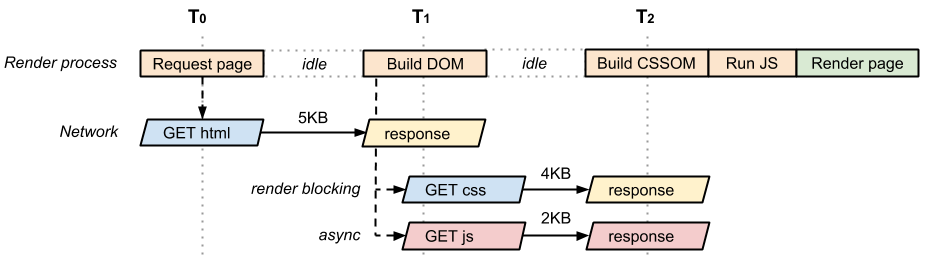
- 在瀏覽器完成 HTML parsing,DOM 建立完畢之後
- 避免 parser blocking,造成 critical rendering path 中的畫面載入延遲
- 加上
async或defer;兩種 attribute 的差異是async會讓 JS 在 parse 完畢後馬上執行,而defer會讓 JS 在 HTML 文件 parse 完、DOMContentLoaded前執行
筆記
預設行為
When the HTML parser encounters a
scripttag, it pauses its process of constructing the DOM and yields control to the JavaScript engine; after the JavaScript engine finishes running, the browser then picks up where it left off and resumes DOM construction.
By default, JavaScript execution is parser blocking: when the browser encounters a script in the document it must pause DOM construction, hand over control to the JavaScript runtime, and let the script execute before proceeding with DOM construction.
- 在預設狀態下,瀏覽器在解析(parse)HTML 文件時如果遇到
script標籤,會暫停解析、改去執行script中的內容;script裡面的內容被執行完畢後,瀏覽器才回頭繼續處理還未完成的 HTML parsing 作業 - JavaScript 會造成 parser blocking
Before the browser can render a page it has to build the DOM tree by parsing the HTML markup. During this process, whenever the parser encounters a script it has to stop and execute it before it can continue parsing the HTML. In the case of an external script the parser is also forced to wait for the resource to download, which may incur one or more network roundtrips and delay the time to first render of the page.
What if the browser hasn’t finished downloading and building the CSSOM when we want to run our script? Answer: the browser delays script execution and DOM construction until it has finished downloading and constructing the CSSOM. JavaScript execution pauses until the CSSOM is ready.
CSS Object Model (CSSOM) is transformed from CSS markup.
CSS is render blocking: the browser blocks page rendering until it receives and processes all of the CSS. CSS is render blocking because rules can be overwritten, so the content can’t be rendered until the CSSOM is complete.
- 瀏覽器一定會等到 CSS Object Model(CSSOM,瀏覽器透過解析 CSS 樣式表建立之)建立完畢後,才會去執行
script中的內容
解決方式
在script標籤加上async或defer
<script async src="my.js"> /* do something */</script><script defer src="my.js"> /* do something */</script>The difference is that the
asyncscripts will run as soon as they are available, in whatever order they download, whereas thedeferscripts will not run until the page has finished loading, and will run in the order they appear on the page.
async
一旦 JS 解析完畢後,馬上執行
For classic scripts, if the
asyncattribute is present, then the classic script will be fetched in parallel to parsing and evaluated as soon as it is available.
For module scripts, if the async attribute is present then the scripts and all their dependencies will be executed in the defer queue, therefore they will get fetched in parallel to parsing and evaluated as soon as they are available.
This attribute allows the elimination of parser-blocking JavaScript where the browser would have to load and evaluate scripts before continuing to parse. defer has a similar effect in this case.
defer
在 HTML 文件解析完畢後、DOMContentLoaded之前執行
This Boolean attribute is set to indicate to a browser that the script is meant to be executed after the document has been parsed, but before firing DOMContentLoaded.
Scripts with the defer attribute will prevent the DOMContentLoaded event from firing until the script has loaded and finished evaluating.
Scripts with the defer attribute will execute in the order in which they appear in the document.
This attribute allows the elimination of parser-blocking JavaScript where the browser would have to load and evaluate scripts before continuing to parse. async has a similar effect in this case.
The DOMContentLoaded event fires when the initial HTML document has been completely loaded and parsed, without waiting for stylesheets, images, and subframes to finish loading.
Critical rendering path
The Critical Rendering Path is the sequence of steps the browser goes through to convert the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript into pixels on the screen. Optimizing the critical render path improves render performance. The critical rendering path includes the Document Object Model (DOM), CSS Object Model (CSSOM), render tree and layout.