總結
本週重心放在理解公司專案結構以及 TypeScript Generics、Utility types、Basic types 中的any、unknown、never、void以及type與interface之間的比較,筆記以 TS 相關內容為主
Generic
Generic Types
-
用
<Type>(或時常簡寫為<T>)這種特殊變數來儲存「變數的類型」 -
<T>的功能是「保存變數的類型」,不會處理、保證「保存變數的類型」以外的事;以下程式碼會報錯,就是因為無法保證傳入的變數一定會有length這個 property:function loggingIdentity<T>(arg: T): T {console.log(arg.length);// Property 'length' does not exist on type 'Type'.return arg;}改為以下即可執行,因為參數被限定為陣列類型的資料了:
// 限定傳入的會是「包含單一類型資料的陣列」function loggingIdentity<T>(arg: T[]): T[] {console.log(arg.length);return arg;}// 限定傳入的會是「包含單一類型資料的陣列」function loggingIdentity<T>(arg: Array<T>): Array<T> {console.log(arg.length);return arg;} -
在 interface 上使用
<T>,即可直接觀察到資料的類型:interface GenericIdentityFn<T> {(arg: T): T;}function identity<T>(arg: T): T {return arg;}// 指定傳入的參數一定是number typelet myIdentity: GenericIdentityFn<number> = identity;console.log(myIdentity(4)); // 4
Generic classes
Generic classes are only generic over their instance side rather than their static side, so when working with classes, static members can not use the class’s type parameter.
Class: static keyword
Static methods are often utility functions, such as functions to create or clone objects, whereas static properties are useful for caches, fixed-configuration, or any other data you don’t need to be replicated across instances.
簡單記法:有static關鍵字的話,可以直接透過該 class 取用,不用先new一個該 class 的 instance 出來(如以下示範碼的displayName與logDisplayName());如果沒有static的話,必須透過該 class 的 instance 才能操作(如以下示範碼的bark())
class Dog { static displayName = "A Dog.";
static logDisplayName() { console.log(this.displayName); }
bark() { console.log("Bark!"); }}
let d = new Dog();
d.bark(); // 'Bark!'
Dog.logDisplayName(); // 'A Dog.'Dog.bark(); // Error: Dog.bark is not a functionGeneric Constraints
簡單總結:透過關鍵字extends對傳進來的參數的<T>做出一些限制
interface Lengthwise { length: number;}
// 確保傳進來的參數一定會有length這個propertyfunction loggingIdentity<T extends Lengthwise>(arg: T): T { console.log(arg.length); return arg;}
loggingIdentity(3); // 會報錯,'3'並沒有length這個propertyloggingIdentity({ length: 10, value: 3 }); // 這樣OK,因為傳入的參數有length這個property組合技:
function getProperty<T, Key extends keyof T>(obj: T, key: Key) { return obj[key];}
let x = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4 };
getProperty(x, "a"); // OKgetProperty(x, "m"); // 這個會報錯,因為傳入的obj裡面沒有m這個key解說:
- 透過
keyof取傳入的物件參數的所有 keys - 型別變數
<key>為「物件參數所有 keys 的延伸」 - 對於傳入的
key參數的限制為「只能是該物件參數的 keys」
keyof Type Operator
The
keyofoperator takes an object type and produces a string or numeric literal union of its keys.
簡單來說:抓某物件的 keys 作為 type
type Point = { x: number; y: number };type P = keyof Point; // P會是 'x' | 'y'
let p: P = "x"; // 變數p只能是'x'或'y',其他都會報錯typeof Type Operator
Specifically, it’s only legal to use typeof on identifiers (i.e. variable names) or their properties.
簡單來說:把它變成 type
function f() { return { x: 10, y: 3 };}
// 這樣會報錯type P = ReturnType<f>;
// 要這樣寫,透過typeof取出f的type// type P = { x: number; y: number; }type P = ReturnType<typeof f>;type any
- 可以 compile,TS compiler 會跳過 type checking(
@ts-ignore),但執行時就有機會出錯 - 基本上就像是原生 JS
- 在 TS 無法透過上下文推論出類型時,會帶入 type
any(When you don’t specify a type, and TypeScript can’t infer it from context, the compiler will typically default toany.)
type unknown
The
unknowntype is a lot safer than any becauseunknownforces us to do additional type-checking to perform operations on the variable.
- TS compiler 在使用者直接操作
unknown類型的資料時會報錯(Theunknowntype represents any value. This is similar to theanytype, but is safer because it’s not legal to do anything with anunknownvalue.) - 搭配 type narrowing 或 type assertion(anUnknownVariable as string)使用(No operations are permitted on an
unknownwithout first asserting or narrowing to a more specific type.)
type never
-
Indicates a function that never returns.
function throwUserNotFoundError(userId: number): never {throw new Error(`User with id ${userId} is not found`);}function infiniteLoop(): never {while (true) console.log("infinite loop");} -
Also, the TypeScript compiler asserts the
nevertype if we create an impossible type guard.const uncertain: unknown = "Hello world!";if (typeof uncertain === "number" && typeof uncertain === "string") {console.log(uncertain.toLowerCase());}// 會報錯:Property ‘toLowerCase’ does not exist on type ‘never’.
type void
- A function that does not return any value explicitly has a return value of
undefined. To indicate that we ignore the return value, we use thevoidreturn type.function greeting(): void {console.log("hi there!");}
void !== undefined
When a function’s return value set as void, this also means that don’t use the return value of this function.
declare function forEach<T>(arr: T[], callback: (el: T) => undefined): void;
let target: number[] = [];forEach([1, 2, 3], (el) => target.push(el));// 這樣會報錯:Type "number" is not assignable to type "undefined"// 因為Array.prototype.push()會回傳陣列的長度,陣列長度不是undefined.// 這樣就可以declare function forEach<T>(arr: T[], callback: (el: T) => **void**): void;
let target: number[] = [];forEach([1, 2, 3], el => target.push(el));type vs interface
The key distinction is that a type can NOT be re-opened to add new properties vs an interface which is always extendable.
If you would like a heuristic, use
interfaceuntil you need to use features fromtype.
interface: always extendable
以下寫法等於是延伸了 interface Point 的內容,最後 interface Point 的 z 值被視為 optional,故傳入的物件有無包含 z 都不會報錯:
interface Point { x: number; y: number;}
// 可以直接沿用同一個interface,追加新的內容interface Point { z?: number;}
function printCoord(pt: Point) { console.log("The coordinate's x value is " + pt.x); console.log("The coordinate's y value is " + pt.y);
if (pt.z) console.log("The coordinate's z value is " + pt.z);}
printCoord({ x: 100, y: 100 });printCoord({ x: 100, y: 100, z: 123 }); // 這樣不會報錯但會建議使用 extends 關鍵字來延伸 interface 內容,增加閱讀性,也減少意外覆蓋的可能性
type: can NOT be re-opened
以下這樣會報錯:Duplicate identifier 'Animal'.,type 變數不可重複 assign value:
type Animal = { name: string;};
type Animal = { species: string;};Custom primitives name (type only)
Interfaces may only be used to declare the shapes of objects, can NOT rename primitives.
// 可以透過type來為primitive type自訂新名稱type SanitizedString = string;type EvenNumber = number;
// 這樣不行,會報錯interface X extends string { // ...}- interface 只能描述物件,無法描述原始型別(Primitive)、列舉(Enum)、元組(Tuple)和複合型別
- type 可以描述任何型別
IDE 中是否顯示名稱
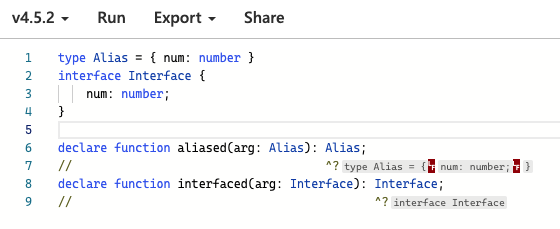
- type 不會創建新名稱
- 故 interfaced 會回傳 Interface(新名稱),而 aliased 會回傳
{ num: number }(而非 Alias)