本筆記的內容出自影片 What is DDD - Eric Evans - DDD Europe 2019,我認為地圖很適合用來解釋 DDD 中領域(domain)與模型(model)代表的意義。
文字定義
- 領域:代表一個範圍內的知識或活動
- 模型:將一個領域中的特定片段抽象化
地圖比喻
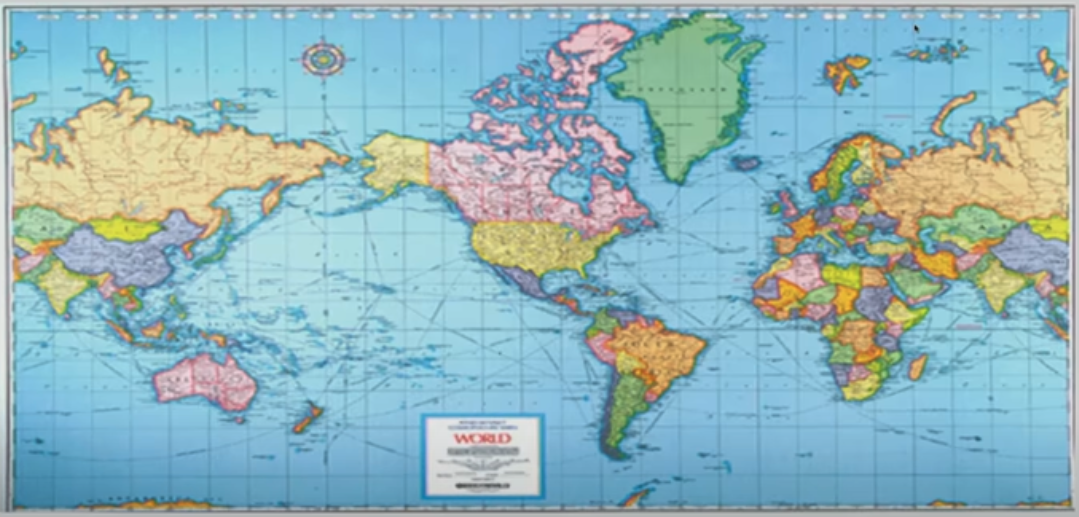
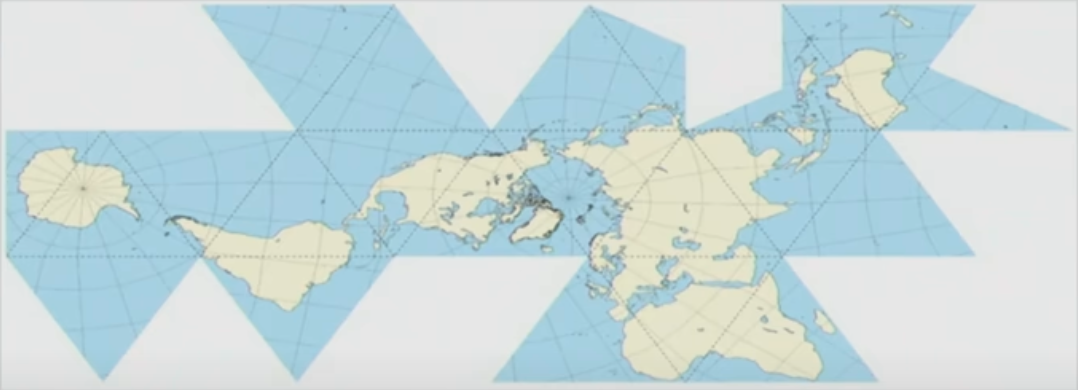
全球地圖(world map)會告訴讀者「如果把地球畫在紙上,會是什麼樣子」,且會有不同的繪製方式。下方第一張是使用麥卡托投影法(Mercator projection)繪製的地圖、第二張是使用摩爾威特投影法(Mollweide projection)製作:
而當我要回答以下問題時,地圖的繪製方式會影響作答的難易程度:
- 從香港到西雅圖的航線方向是?
- 格陵蘭與非洲的面積差距是?
第一張地圖能讓人一筆就畫出香港到西雅圖的航線,但第二張地圖就無法簡單地回答這個問題。
反之,當我想確認格陵蘭與非洲的面積差距時,只看第一張地圖是不可能給出正確答案的——但是摩爾威特投影法此時就能發揮功能了,第二張地圖能讓我相對精確地估算兩處的面積差異。
這就是透過地圖來比喻領域(domain)與模型(model)分別是什麼——地圖描述了關於地球表面的知識,而各種投影法用不同的方式描述關於地表的資訊。
並且你會注意到,不同模型各有其擅長解決的問題。
影片摘要(英文)
名詞定義
- domain: a sphere (範圍) of knowledge or activity
- model: a system of abstractions representing the selected aspects of a domain
- a model distills (抽取、提煉) knowledge and assumptions about a domain
- a model describes a very specific problem you’re solving
從領域到模型
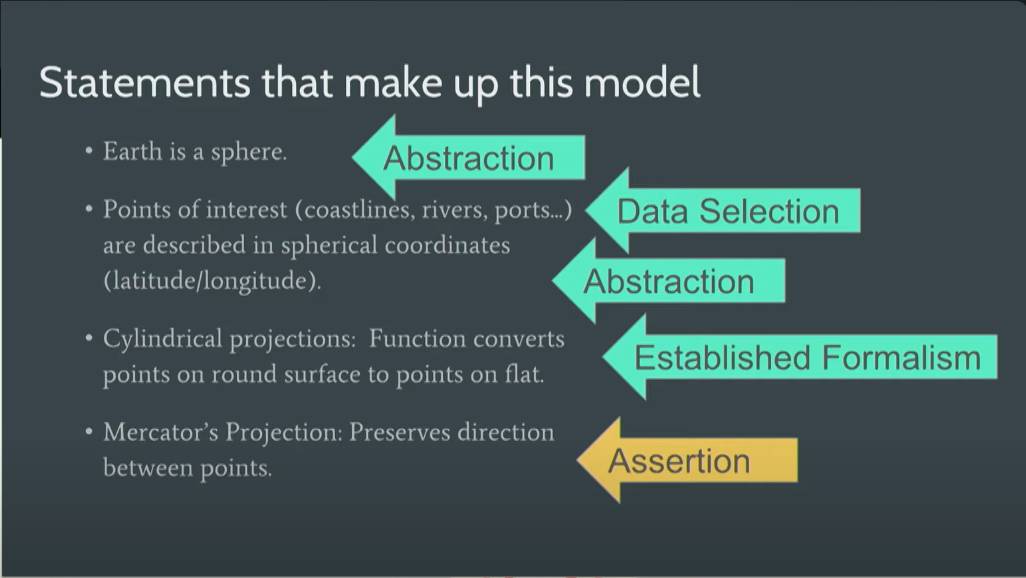
- Abstraction: Earth is a sphere.
- Selection & Abstraction: Points of interest (coastlines, rivers, posts…) are described in spherical coordinates (latitude/longitude).
- Established Formalism: Cylindrical projections — function converts points on round surface to points on flat.
- Assertion: Mercator Projection — preserves direction between points.