總結
此篇文章是 Good Code, Bad Code: Think like a software engineer 第三章(How to learn programming syntax quickly)的閱讀筆記。章節重點包含:
- 為何推薦記憶(背誦)程式碼語法
- 如何強化記憶
- 學習新程式碼語法、概念的技巧
筆記
為何背誦
承前面章節提及過的重點:一個工程師腦中已知的語法、程式相關碼知識越多,越能幫助工程師理解一段程式碼。理由是人類的短期記憶空間有限,但可以搭配長期記憶中的知識來分塊(chunking)透過視覺接收到的內容,從而讓理解一大段程式碼更為輕鬆。
What you already know impacts to a large extent how efficiently you can read and understand code. The more concepts, data structures, and syntax you know, the more code you can easily chunk and thus remember and process.
而可能有讀者會提出疑問:遇到不熟悉的內容時,透過網路查詢相關資訊也不是什麼難事,為什麼需要花費額外的精力來記憶這些內容呢?
書中提出的理由是:
- 停止閱讀、轉去查詢資料這個動作會打斷你的思考流程,而每經歷一次「中斷」,通常需要消耗 15 分鐘來回到中斷前的狀態
- 「記憶」這件事情需要有意識的練習,如果你選擇不去刻意記得這次查詢到的結果,那麼下次遇到一樣的程式碼時,你還是得花時間來查找資料
因此,作者認為花費一些心思來記憶程式碼語法是一個有利於工程師的行為。
如何強化記憶
本書對於「強化記憶」的定義:記得更久、更容易回想已經記住的內容。為了滿足前述需求,本書提出兩種練習方式:檢索練習(retrieval practice)與加工練習(elaboration practice)
retrieval practice
實行方式:如其名,在遇到一個不熟悉的概念時,在查看解答前,先試圖從腦中回想已知的部分。這個「試圖回想」的動作就能強化大腦「執行檢索」的能力。
When you try to remember a fact that you know you know, without extra study, you improve retrieval strength ability.
elaboration practice
參考下圖,記憶在人腦中會以圖右的「連結」形式存在。在學習新知時,如果能夠把「新知」與「已知」進行連結,則這份新知有更高的機會可以在腦中保存得比較久。
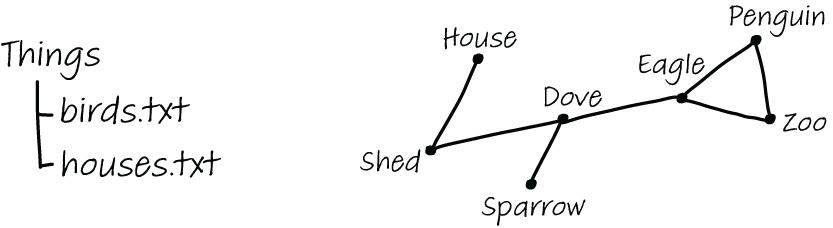
Elaboration means thinking about what you want to remember, relating it to existing memories, and making the new memories fit into schemata already stored in your LTM.
When you learn new information, you will try to fit the information into a schema in your brain before storing it in LTM. Information that fits an existing schema better will be easier to remember.
總結:學習技巧
作者推薦使用小卡:正面寫下「想要記得的程式碼概念、語法」,背面寫出該概念的說明、或是某語法的書寫方式。
練習的方式為:閱讀小卡正面的內容,並試圖寫下、或完整闡述小卡上記載的程式碼知識。注意:就算一看到題目就知道自己無法順利回答也不要直接翻開答案,請盡可能努力回想腦中已有的資訊。因為這個「回想片段資訊(retrieval practice)」的過程也能強化我們對該概念的理解,強化要記住的內容。
學習的頻率:比起一口氣背誦大量知識,更有效的做法是少量多餐、但間隔一段時間後固定進行複習。「固定複習」能夠強化「取出腦中特定知識」的流暢度。